Applications for Macintosh
cdem
Stereonet3D
GeoKalk
SSPX
Trishear3D
Backstrip
Flex2D

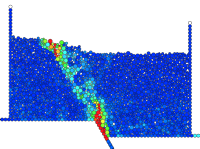
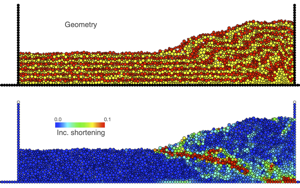
cdem is a macOS application for 2D discrete element modeling of geological structures and their deformation. cdem integrates pre-processing, processing, and post-processing (visualization) in a single application. To learn more about cdem, please check our paper in Geosphere and Stuart Hardy at LinkedIn.
Out of courtesy, please let us know you have downloaded the program.

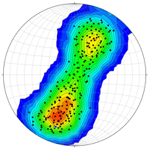
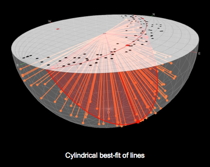
Stereonet3D can perform various operations, including calculating poles to planes, rotating planes and lines, constraining lines to lie on their planes, angle between lines or planes, cylindrical best fit, conical best fit, and mean vector. Data with lat-long information can be exported to Google Earth.
To test the program's Map view and export to kml, here are two files with strike/dip data from the Big Elk anticline in SE Idaho, and locations in lat-long or UTM (right click to download and open with the program's File -> Load Dataset from txt menu).

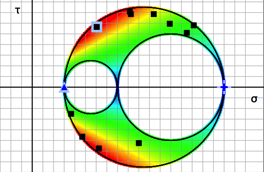
GeoKalk was made for geologists, but it can be used by anyone interested in vectors and tensors. GeoKalk runs on Mac OSX 10.9 or later. It is freely available on the Mac App Store.

Here you can find some GPS and DEM files to test the program.

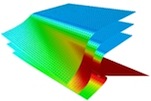
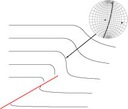
Trishear3D runs on Mac OSX 10.9 or later. The program is free for non-profit purposes (for consulting please contact me).

version 7.1, August 9, 2021

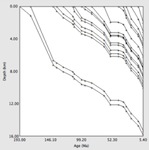
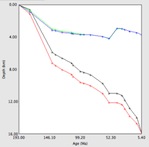

version 5.3, August 15, 2022
Backstrip is an Intel Application
On M1 Macs, it runs under Rosetta

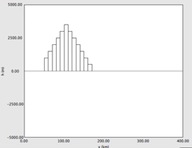
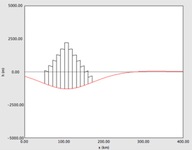

version 5.2, August 15, 2022
Flex2D is an Intel Application
On M1 Macs, it runs under Rosetta



