 OverlappingFrame
OverlappingFrame
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||
java.lang.ObjectOverlappingFrame
This software is still under development.
Note that the term frame in this context has a mathematical meaning,
it is an extension of the mathematical term basis.
It has no connection to the class java.awt.Frame.
Overlapping frame.
See also documentation for class BlockFrame.
An overlapping frame is an extention (generalization) of a block-oriented frame.
The frame size is given by N, K and P
(the overlapping factor, for P=1 it reduces to the block-oriented frame).
An overlapping frame can be regarded as an infinite large block oriented frame.
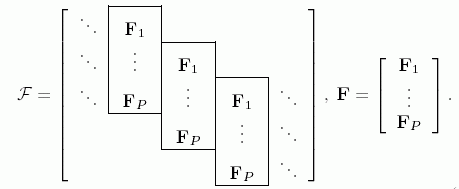
In practise it is as large as necessary depending on the signal length.
For the case with circular extension, and the length of the one-dimensional signal is NL,
then the large overlapping frame will be a matrix of size NL×KL, built by
repeating the frame block F1, F2 and F3, each of size N×K.
The structure, with P=3 and numbering from 0 to (P-1) instead of from 1 to P, is:
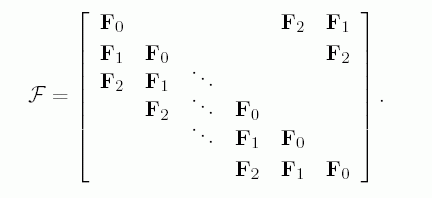
| Constructor Summary | |
OverlappingFrame(BlockFrame fb)
Constructs an overlapping frame by repeating the block-oriented frame. |
|
OverlappingFrame(int sizeN,
int sizeK,
int sizeP)
Constructs an overlapping frame with random values. |
|
OverlappingFrame(int sizeN,
int sizeK,
int sizeP,
double[] val)
Constructs an overlapping frame with values from given array. |
|
| Method Summary | |
double[] |
circMult(double[] w)
The matrix F is formed as a circular extension of the overlapping frame, then multiplies the matrix F (the frame) by array w
and returns the result in an array.
|
void |
circTrMult(double[] r,
double[] c)
The matrix F is formed as a circular extension of the overlapping frame, then multiplies the transposed of matrix F (the frame) by array r
and store the result in array c. |
double |
getIpValue(int k1,
int k2)
Returns the inner product of two frame vectors. |
int |
getIterationsDone()
Returns number of iterations done in last call to vsMblock. |
int |
getK()
Returns frame size variable K, number of frame vectors. |
java.lang.String |
getLastMessage()
Returns the last message generated, i.e. error, warning or information message. |
int |
getN()
Returns frame size variable N. |
int |
getP()
Returns frame size variable P, overlapping factor. |
double |
getProbEst()
Returns estimated probability for improvement of last call to vsMblock. |
int |
getQ()
Returns frame size variable Q, total number of variables in the frame. |
int |
getSupportEnd(int k)
Returns the support end position of a frame vector. |
int |
getSupportLength(int k)
Returns the support length of a frame vector. |
int |
getSupportStart(int k)
Returns the support start position of a frame vector. |
double |
getValue(int k,
int n)
Returns an entry (a value) in the frame. |
boolean |
isUniform()
Tells if frame is uniform, i.e. the norm of all frame vectors is one, or not. |
void |
makeUniform()
Makes the frame uniform. |
void |
mult(double[] w,
double[] xr)
The matrix F is formed as a simple extension of the overlapping frame, then multiplies the matrix F (the frame) by array w
and store the result in array xr. |
void |
setVerboseLevel(int level)
Set how verbose functions in this class are on information-, warning- and error-messages. |
void |
trMult(double[] r,
double[] c)
The matrix F is formed as a simple extension of the overlapping frame, then multiplies the transposed of matrix F (the frame) by array r
and store the result in array c. |
double[] |
vsGMP(double[] x,
int S)
vsGMP (Global Matching Pursuit) does the Basic Matching Pursuit algoritm where the (huge) matrix F is formed as a circular extension of the overlapping frame. |
double[] |
vsMblock(double[] x,
double[] w,
int M,
int alg,
int maxIt,
double probLimit)
vsMblock does vector selection by dividing the overlapping frame into blocks. |
double[] |
vsMblock(double[] x,
int S,
int M)
vsMblock does vector selection by dividing the overlapping frame into blocks. |
| Methods inherited from class java.lang.Object |
clone, equals, finalize, getClass, hashCode, notify, notifyAll, toString, wait, wait, wait |
| Constructor Detail |
public OverlappingFrame(int sizeN,
int sizeK,
int sizeP)
sizeN - sizeK - number of frame vectorssizeP -
public OverlappingFrame(int sizeN,
int sizeK,
int sizeP,
double[] val)
sizeN - sizeK - number of frame vectorssizeP - val - the NPK values (ordered by column, i.e. by frame vectors)
The frame is organized as a matrix of size NP×K and then formed
into a vector (of size NPK×1) column by column.public OverlappingFrame(BlockFrame fb)
| Method Detail |
public int getN()
N.
public int getK()
K, number of frame vectors.
public int getP()
P, overlapping factor.
public int getQ()
Q, total number of variables in the frame.
public java.lang.String getLastMessage()
public boolean isUniform()
public int getIterationsDone()
public double getProbEst()
public double getValue(int k,
int n)
k - frame vector number (column in frame) 0 <= k <= (K-1)n - position in frame vector (row in frame) 0 <= n <= (NP-1)public int getSupportLength(int k)
k - frame vector number (column in frame) 0 <= k <= (K-1)public int getSupportStart(int k)
int n = getSupportStart(k);
double v = getValue(k, n);
v contains the first non-zero value of the frame vector.
We will have 0 <= n <= (NP-1).
k - frame vector number (column in frame) 0 <= k <= (K-1)public int getSupportEnd(int k)
int n = getSupportEnd(k);
double v = getValue(k, n-1);
v contains the last non-zero value of the frame vector.
We will have 1 <= n <= NP. (The case n==0 would indicate
an all zero frame vector, and then it should not be in the frame.)
k - frame vector number (column in frame) 0 <= k <= (K-1)
public double getIpValue(int k1,
int k2)
k1 - number for the first frame vector (column in frame)k2 - number for the second frame vector (column in frame)public void setVerboseLevel(int level)
level - indicate how verbose the functions in this class are
public void makeUniform()
public void circTrMult(double[] r,
double[] c)
r
and store the result in array c. The matrix F is
the matrix implicit given by setting the frame vectors as the columns of F.
c=F'*r
and the sizes are: c is KL×1, F is NL×KL, r is NL×1.
r - the signal (residual) that is multiplied by the frame. It is unchanged.c - the results. It is created if needed, and its values are set.
public void trMult(double[] r,
double[] c)
r
and store the result in array c. The matrix F is
the matrix implicit given by setting the frame vectors as the columns of F.
c=F'*r
and the sizes are: c is KL×1, F is N(L+P-1)×KL, r is N(L+P-1)×1.
r - the signal (residual) that is multiplied by the frame. It is unchanged.c - the results. It is created if needed, and its values are set.public double[] circMult(double[] w)
w
and returns the result in an array.
The corresponding code i Matlab notation would be: xr=F*w
and the sizes are: w is KL×1, F is NL×KL, xr is NL×1.
The resulting vector (represented as an array) is formed as a linear combination
of the frame vectors where the coefficients are given by the weights w.
w - contains the weights that are multiplied by the frame vectors.
public void mult(double[] w,
double[] xr)
w
and store the result in array xr.xr=F*w
and the sizes are: w is KL×1, F is N(L+P-1)×KL, xr is N(L+P-1)×1.
The resulting vector (represented as an array) is formed as a linear combination
of the frame vectors where the coefficients are given by the weights w.
w - contains the weights that are multiplied by the frame vectors. It is unchanged.xr - the results (reconstructed signal). It is created if needed, and its values are set.
public double[] vsGMP(double[] x,
int S)
x - the signal to be approximated by the sparse representation.
It is unchanged, size is NL×1.S - allowed number of non-zeros weights in w, or frame vectors used.
public double[] vsMblock(double[] x,
int S,
int M)
x - the signal to be approximated by the sparse representation.
It is unchanged, size is NL×1.S - allowed number of non-zeros weights in w, or frame vectors used.
Appropriate (i.e. tested) range for S should be such that
0.02 <= S/NL <= 0.25 and must be 0 < S < NLM - How many times the overlapping frame is repeated in the block.
public double[] vsMblock(double[] x,
double[] w,
int M,
int alg,
int maxIt,
double probLimit)
x - The signal to be approximated by the sparse representation.
It is unchanged, size is NL×1.w - The initial weights, size is KL×1.M - How many times the overlapping frame is repeated in the block.alg - Indicate which algorithm to use for vector selection for one block.
See class BlockFrame for description of these algorithms.
maxIt - Maximum number of iterations to do, i.e. max number of blocks to
make and process.probLimit - The probability that the next iteration
will find better weights and thus improve the sparse representation is
estimated after eachiteration.
The (intern) variable probEst is an estimate for the
probability that the next iteration will give an improved representation.
After each iteration probEst is updated, and if
probEst < probLimit the function is finished.
As long as every iteration improves the representation probEst=1.
We should have 0 < probLimit < 1.
|
||||||||||
| PREV CLASS NEXT CLASS | FRAMES NO FRAMES | |||||||||
| SUMMARY: NESTED | FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | DETAIL: FIELD | CONSTR | METHOD | |||||||||