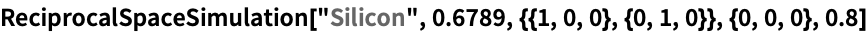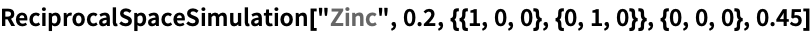MAXRD SYMBOL
ReciprocalSpaceSimulation
ReciprocalSpaceSimulation[crystal,{L1,L2},origin,dmin]
plots a simulation of the reciprocal space of crystal, with L1 and L2 defining the layer plane centred at origin and dmin the resolution.
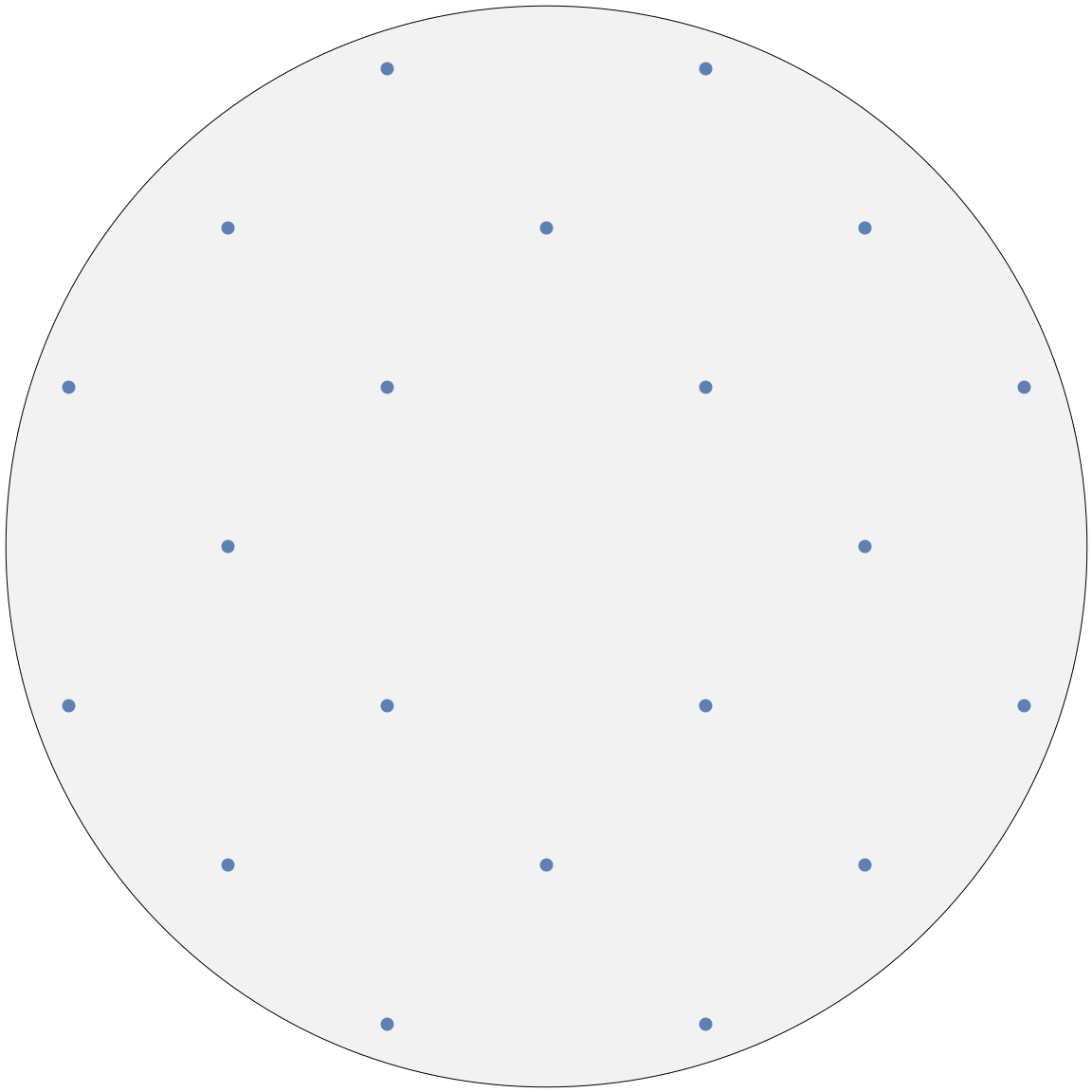
ReciprocalSpaceSimulation[crystal,λ,{L1,L2},origin,dmin]
plots a simulation of the reciprocal space of crystal at wavelength λ, with L1 and L2 defining the layer plane centred at origin and dmin the resolution.